B
Basil Hadjirafael
Obstetrician Gynecologist Surgeon, Robotics,
Laparoscopic Surgery
Hysteroscopy is a simple and painless method with a very high diagnostic capacity.
There are two types of hysteroscopy, diagnostic and interventional hysteroscopy.
 1. DIAGNOSTIC HYSTEROSCOPY
1. DIAGNOSTIC HYSTEROSCOPY
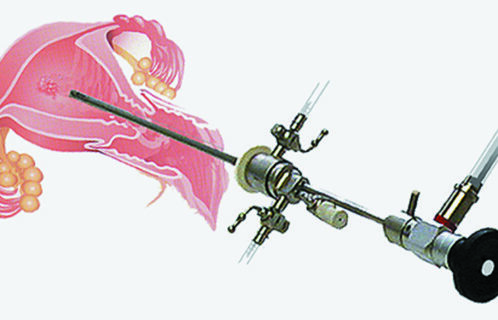
It is a method that allows us to check the inner cavity of the woman’s uterus (endometrium) without having to make incisions. The gynaecologist inserts a very small camera from the vagina into the endometrial cavity and views the endometrium in detail. It usually does not require anesthesia and is very well tolerated by the patient.
With this examination we check the endocervix for polyps, adhesions or malignancy, and the uterine cavity for the presence of a diaphragm, abnormalities of the uterus, adhesions, fibroids, polyps, hyperplasia and malignancy.
Diagnostic hysteroscopy is also necessary in cases of infertility. It is also needed before the IVF procedure.
2. INVASIVE HYSTEROSCOPY
It is the method used exclusively for surgical procedures inside the uterine cavity such as:
– Endometrial polyps
– Solution of adhesions
– Matrix diaphragm
– Fibroids
– Biopsy under visual inspection for the possibility of endometrial malignancy
– Therapeutic removal of the endometrium in uterine bleeding very common in the menopause or menopause.
Invasive hysteroscopy is performed in the operating room under light anesthesia (intoxication). The gynaecologist inserts from the vagina into the patient’s uterus only a very thin instrument together with the camera, looks exactly at the location of the morphoma (polyps, fibroids, adhesions) and removes it from the vagina, without any incision in the abdomen.
Which days of the cycle are suitable for hysteroscopy?
In women of reproductive age, hysteroscopy is performed after the end of the period, i.e. the 4th-8th day of the cycle (depending on the cycle of each woman). In menopausal women, it can be done on any day.
How long does the hospital stay last?
Usually the woman does not need to stay in hospital for more than an hour after the operation and returns to her activity without restriction.
Can curettage replace hysteroscopy?
Hysteroscopy is a very specialized and unique method for the removal of polyps, fibroids, adhesions and diaphragm lysis as well as for localized biopsy or therapeutic removal of the endometrium and can never be replaced by uterine curettage. The big difference between uterine curettage and hysteroscopy is that: a) curettage is a blind method, i.e. there is no visual image of the inside of the uterus and b) in curettage no diathermy is used, so no tissue can be cut and removed (e.g. fibroid, polyp, symphysis, uterine septum).